Thinking more mobile: How controllers are revolutionizing robot control
Whether on rails, rollers or arms: Modern robots need control centers that think with them – and move with them and humans.
The requirements in robotics are increasing. Robot arms and systems are increasingly taking on complex tasks and need to be flexibly integrated into industrial processes. At the same time, expectations of the robot controller are growing: it should not only be powerful and robust, but also mobile, modular and capable of adapting to a wide variety of environments and applications. This is where handheld robot controllers and portable robot controllers come in – they form the technological heart of modern automation solutions. If you want to automate flexibly and efficiently today, you need more than just computing power: you need mobility, intelligent control units, genuine networking and real intelligence in an industrial environment.
Flexible robot controllers for flexible automation
Industrial robotics is going through a period of upheaval. Advancing automation and the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in production processes are turning modern industry upside down. Instead of rigid production lines and permanently installed robotic arms, mobile, collaborative and scalable systems are increasingly being used. However, the growing demand for agility requires more than just mechanical innovations - new control concepts are needed. The central question is: how can robots be efficiently trained, controlled and maintained when they are no longer stationary?
This is exactly where modern robot controllers come into play. These control units are compact, robust and extremely flexible. They can be used on robot arms, on driverless transport systems or within compact production cells - and thus enable real-time control directly in the action. As a central control unit, they support modern HMI concepts and increase machine intelligence at store floor level.
The installation of robot systems, in particular industrial robots, cobots and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), has increased significantly over the last three years. The variety of fields of application has also changed massively. This change requires mobile, robust and flexible controllers. After all, the aim is to further improve Germany's and Europe's competitiveness - with the help of intelligent automation solutions.
Decentralization is the key
Traditional control architectures with central control cabinets are too inflexible for many modern automation scenarios. Decentralization is therefore the order of the day. Robot controllers enable a new modularity in automation: each component - whether gripper arm, inspection camera or motion module - can be given its own intelligence. This distributed logic creates adaptive control concepts and reduces integration costs.
The advantages:
- Faster integration of new modules into existing systems
- Better scalability with increasing levels of automation
- Minimized failure risks thanks to distributed control logic
- Independence from central infrastructures
The result is adaptable, resilient automation networks that can be flexibly adapted to changes in production.
Edge computing as a game changer
In many applications, milliseconds are crucial - for example in safety reactions, image processing or interaction with people. Robot controllers bring computing power directly to the point of action. They enable edge computing: data is not sent to a central location for processing, but evaluated locally. This local intelligence is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0.
Advantages of the edge approach:
- Minimal latency for fast responses
- Reduced network load due to local data processing
- Greater reliability in the event of connection failures
- Data sovereignty in sensitive applications
This proximity to the data source is particularly crucial in safety-critical scenarios or for AI-supported systems (e.g. optical inspection or object recognition).
Precision and efficiency
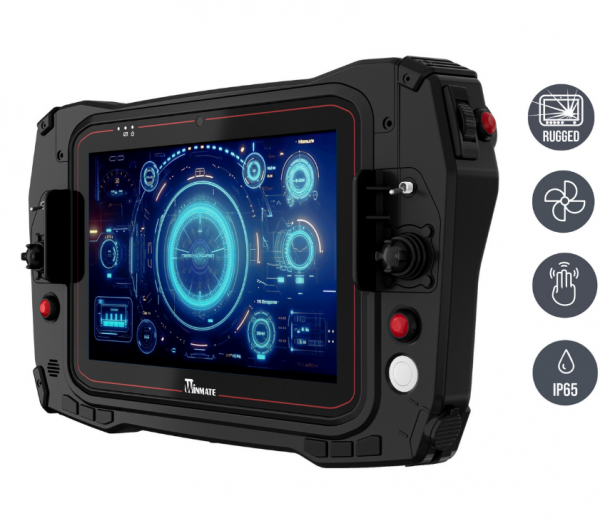
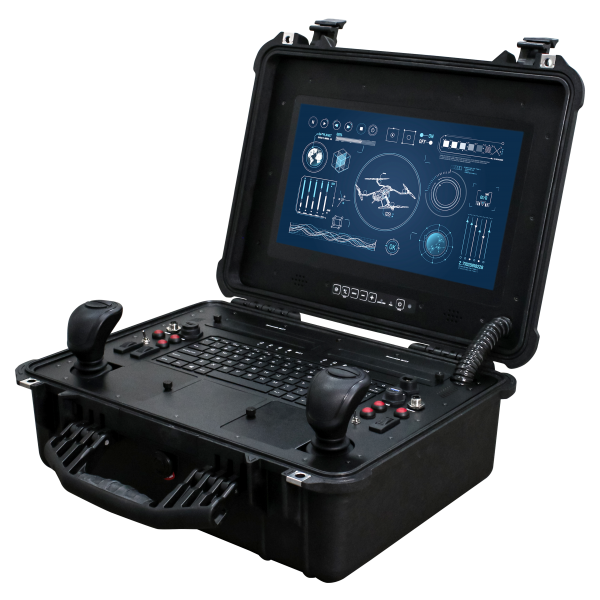
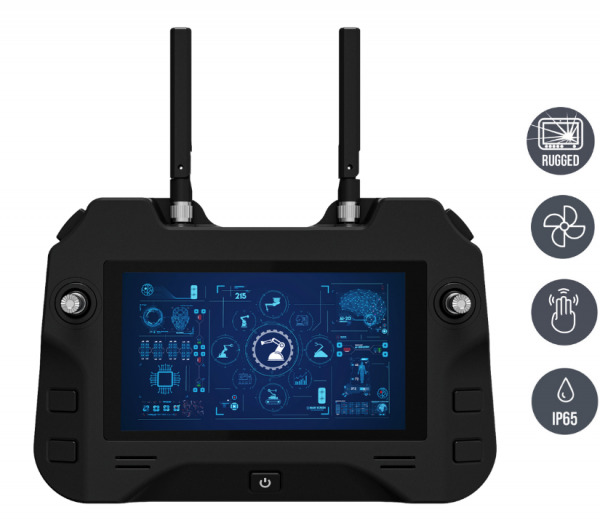
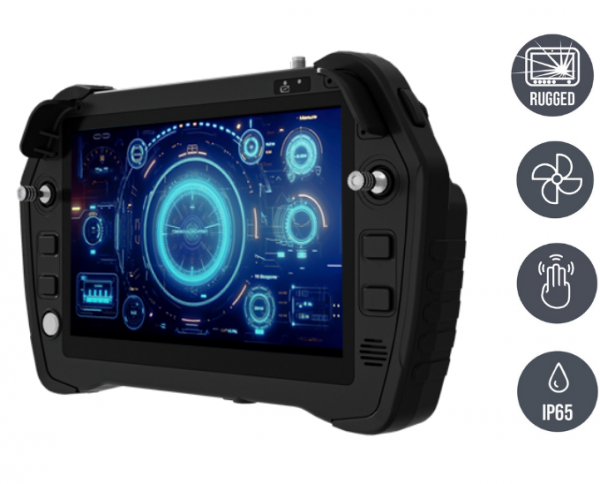
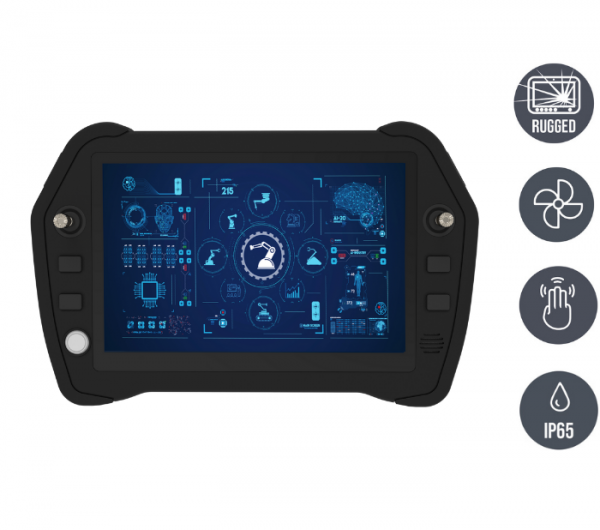
Of course, mobile robot controllers (handheld or portable) should have a user-friendly interface and advanced control functions that facilitate operation and increase efficiency. Even better is intuitive operability through customizable joysticks and toggle switches. This also minimizes the training period enormously.
Many robots, especially in manufacturing or autonomous operation, have built-in cameras as “eyes” for environment and object recognition, navigation or quality inspection. Consequently, controllers must be able to process image data in real time using a software-based decoder to enable better and faster decisions. The software decoder works differently than a hardware decoder, which uses dedicated chips or specialized hardware to decode video data. The software decodes compressed video stream formats such as H.264, H.265 or MUPEG into raw data on the controller's CPU.
Important requirements:
- Low latency during decoding
- High processing performance with simultaneous power-saving operation
- Reliable integration with camera and sensor systems
This also makes it clear that the controller display is also becoming the central playing field. This is desirable:
- Low-reflection, projected-capacitive multi-touch displays
- Operability with gloves
- Readability in extreme light or sunlight
- Resolution of 1920 × 1200 pixels in 16:10 format
Robust technology for harsh conditions
Industrial environments are rarely ideal: dirt, dust, vibration, heat or cold place enormous demands on any electronics. Robot controllers must therefore be designed to function reliably under extreme conditions. Their hardware platform must be designed to be durable and maintenance-free - even as a mobile control solution in the field.
Typical features:
- Fanless design for freedom from maintenance
- Shock and vibration resistant housing
- Extended operating temperature ranges (-20 °C to +60 °C)
- IP65/IP67-certified variants for direct machine integration
- Flexible power supply for mobile applications
Safety and standard requirements
Controllers in robotics must also meet high safety standards. Standards such as ISO 10218 for robots and ISO/TS 15066 for collaborative robots specify how controllers can make collaboration between humans and robots safe and efficient. Mobile robot controllers often integrate emergency stop mechanisms that enable an immediate response in the event of a failure and thus prevent accidents.
Another important element is certification:
- Z. E.g. ATEX certification for potentially explosive atmospheres
- Approval for international use (e.g. CE, UL, FCC)
Networking without limits
Modern robotic controllers are real communication talents. They master a wide range of industrial protocols - and can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks:
- Real-time Ethernet (PROFINET, EtherCAT, Modbus TCP)
- Serial communication (RS-232/422/485)
- Digital and analog I/Os
- USB 3.0, HDMI, PoE
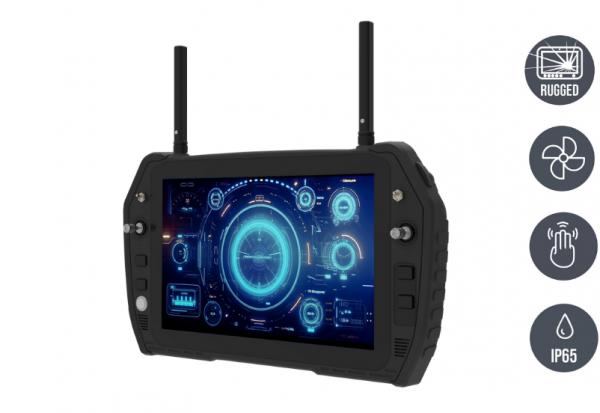
- Wireless standards such as WiFi, Bluetooth, LTE/5G
This variety of connections makes it possible to connect sensors, actuators, human-machine interfaces and higher-level control systems directly – without additional gateways or detours. This allows modern control concepts to be implemented seamlessly.
If you have any special requirements or need advice, we will be happy to help you.
All prices excl. value added tax